Exclusive Neuroject Article: Smart gadgets that can be worn, commonly known as wearable sensors, are gaining popularity both for personal and professional use. These typically consist of clothing items and accessories embedded with cutting-edge electronic tech, frequently offering connectivity with smartphones or the ‘Internet of Things (IoT).
While these wearable devices are often employed to boost health and wellness by assisting in personal fitness routines, their use in tracking occupational safety and health risks is becoming increasingly widespread. Several of these tools have already hit the market, while others are still in the pipeline. As the availability of these wearables expands, they carry the potential to beneficially influence and change the structure of society and professional life as we understand it today.
Building sites are ever-changing spaces with distinct and often dangerous work conditions that may vary on a daily basis and throughout the duration of a project. These sites often subject workers to extreme weather, loud sounds, and poor air conditions. Heavy machinery is often operating near ground workers, presenting possible risks for accidents involving workers and construction vehicles. The temporary and project-based nature of construction sites makes the application of many standard industrial monitoring systems unfeasible. All these factors contribute to a growing need for wearable tech solutions.
Table of Contents
1. Helmet
Protective helmets equipped with tracking sensors. Intelligent boots and timepieces. Spectacles that provide access to augmented reality. Exoskeletons that alleviate user strain. These represent some of the wearable sensors that have surfaced in recent years, designed to enhance safety and efficiency on construction sites for workers and supervisors alike.
TokenMe, a company rooted in the Netherlands, was honored with the Innovation Award for wearable technology at the Consumer Electronics Show in Las Vegas. The company’s offering provides construction managers with a real-time tracking solution for personnel and assets using low-energy, location-conscious radio, and RFID (radio-frequency identification) tags, coupled with multiple sensors. The gathered data is then processed through cloud-based artificial intelligence.
TokenMe’s combined solution is tailored to enhance safety at construction sites. Their system comprises wearable smart badges (tokens), wall-installed sensor hubs (anchors), LoRaWAN gateways, and user-friendly dashboards that operate in unison to deliver real-time data and insights. This pioneering technology paves the way for more effective project management and aids in an accident and injury prevention by delivering a precise overview of the operations on the construction site.
The real-time data features allow supervisors and managers to track worker presence, recognize unauthorized entries into risky areas, and spot potential safety hazards arising from environmental conditions. This information enables those in charge to take swift corrective steps to avoid accidents and uphold a safe working atmosphere. Additionally, the gathered data from these wearable sensors can serve to enhance future projects by spotting trends and patterns, enabling the creation of more informed safety procedures and guidelines.

2. Exoskeletons
The wearable sensors embedded in the robotic innovation of exoskeletons are here for the long haul. It’s taken a couple of decades to reach this juncture, but the assimilation of these potent machines integrated with wearable sensors into the industry in a more efficient and acceptable manner signifies a significant transformation for the future of construction. Much of this change is promising, some of it is exceptional, and all of it is incredibly intriguing.
An exoskeleton, typically a motorized device made of metal, is designed to be worn on a person’s body. It’s engineered to amplify the user’s strength and promote correct body movements, thus making lifting objects less strenuous and reducing the overall bodily strain. The wearable sensors within these exoskeletons are crucial for tracking movements and providing necessary feedback for optimal functionality.
Exoskeletons can be full-body suits or can be crafted to be worn only on specific body parts, such as hands or shoulders. Each exoskeleton type, however, uses wearable sensors to monitor the user’s movements and provide appropriate mechanical assistance.
Exoskeletons are donned to diminish the physical strain caused by performing specific tasks. Their use of wearable sensors allows for precise monitoring and adjustment, ensuring they enhance rather than hinder the user’s natural movements. Initially, exoskeletons were employed in the healthcare sector to aid in rehabilitation. Lately, they’ve been adopted in labor-intensive industries such as construction and manufacturing, where wearable sensors can detect and prevent potential injury incidents, help in lifting and maneuvering hefty items, and offer a robust support structure for handling large machinery and objects.
In recent times, developers have concentrated on smaller, more specific exoskeleton projects that focus on a particular body part, even though full-body suits are also utilized. These projects often utilize wearable sensors to provide finely-tuned assistance and monitoring.
Tool-bearing exoskeletons consist of a spring-activated arm that holds a hefty tool on one side and is linked to a lower-body exoskeleton and a counterweight on the other. The tool’s weight is transferred to the ground. These exoskeletons, often integrated with wearable sensors, are typically passive and might contain only a single joint, which is adequate for providing weight support.
One such example is the EksoZeroG, developed by Ekso Bionics. This mounted-arm exoskeleton isn’t donned on the body. Instead, workers operate the arm by placing their hand at its end. According to Ekso, the exoskeleton, equipped with wearable sensors, aids workers in rapidly utilizing heavy hand tools, enabling them to finish tasks quicker, with less exhaustion, and improved craftsmanship.
3. Smart Glasses
Smart glasses are a type of wearable sensors that transform the physical world into a digital platform. The prototype of this concept can be traced back to Google Glass, a pioneering product that integrated thin frames with an unusual prismatic lens. Despite the initial challenges faced in the consumer market, these wearable sensors have sparked interest in various businesses for their potential use in professional settings.
Fast forward to today, in the realm of construction, smart glasses utilizing wearable sensors have been evolved primarily to augment reality. They offer construction experts the opportunity to walk through high-definition 3D models of building projects, allowing real-time examination and adjustment of virtual components.
Moreover, by integrating wearable sensors in smart glasses with advanced software like Topcon’s, professionals such as surveyors, engineers, and on-site Building Information Modeling (BIM) technicians can achieve improved processing capabilities and cost benefits. The technology permits accurate plotting and measuring of points on a construction site, enhancing precision and efficiency.
Vuzix, a key player in this field, provides safety-rated smart glasses equipped with wearable sensors. These glasses help users maintain safety practices on construction sites by providing hands-free access to data, thereby reducing the need to continuously check a tablet. The fusion of Vuzix Smart Glasses and Topcon’s MAGNET software promises a more productive future for on-site work, keeping projects on track and within budget.

4. Body Wear
For workers at building sites, numerous risks and dangers lurk that could harm them if they aren’t adequately safeguarded. The most prevalent perils include moving objects, falls, trips, vibrations, etc. Among these, the risk of working at significant heights can be mitigated with the appropriate personal protective equipment.
Construction work necessitates a significant amount of equipment, and construction wearables, including wearable sensors, are available for body parts beyond just the wrist, feet, and head. These wearable gadgets enhance safety in several ways, such as monitoring heat levels, detecting gas, and reducing muscle exhaustion.
Heat Tracking: Wearable sensors, which can be worn around the bicep or chest, can identify the core body temperature and notify contractors and workers when a respite in the shade or a sip of water is required.
Gas Detection: Compact wearable sensors that attach to the upper arm or chest can detect a range of hazardous gases, thereby preventing unwarranted exposure and potentially saving lives.
Reduced Muscle Fatigue: A unique technology termed “exoskeletons,” equipped with wearable sensors, can enhance strength and diminish muscle fatigue in several situations, such as heavy lifting or holding tools.
Kenzen, a pioneer in smart Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) with a focus on physiological monitoring and preventing heat-related injuries and fatalities among workers, has introduced a real-time worker heat monitoring system. This cloud-based Software as a Service (SaaS) system incorporates a wearable sensor device that workers wear on their arm. The device, equipped with wearable sensors, alerts both the worker and their supervisor when the core body temperature reaches dangerous levels. Immediate alerts enable timely intervention, enhancing worker safety from heat injuries.

5. Smart Shoes
Every 15 seconds, a worker passes away due to a work-related accident or illness, as reported by a United Nations study. Furthermore, many more suffer long-term consequences from accidents. This is where smart personal protective equipment, incorporating wearable sensors, comes into play, designed with the necessary data to enhance safety at work sites.
An innovative example is Intellinium’s smart boots, which enable workers to exchange messages hands-free, without requiring a smartphone. The alerts can be sent using the company’s patented pressure sensor membrane incorporated into the boot’s toe. These wearable sensors not only promote communication but also provide safety alerts in real-time.
In case of an emergency, workers can confirm receipt of an evacuation message by tapping their toe on the sensor. Furthermore, if they are injured, workers can swiftly send out a distress signal using the wearable sensors.
The integrated wearable sensors register falls or impacts and instantly inform a co-worker or supervisor of the worker’s location. Intellinium—the company behind these smart boots—was established with the explicit goal of enhancing worker safety by merging Internet of Things (IoT) technology, along with wearable sensors, with conventional personal protective equipment.

6. Clip-Ons
Clip-ons are small wearable sensors that can be attached to a worker’s clothing or hard hat. They are designed to improve safety on construction sites by monitoring worker movements and detecting falls. Clip-ons can also help to improve productivity by providing real-time data on worker activity and location. These wearable sensors, though not part of the usual construction PPE, prove very helpful and non-obstructive. They can identify zone-based worker locations and detect free falls.
Triax Technologies is an IIoT platform designed to improve labor productivity and worksite safety. It provides hard-to-capture productivity data and delivers it in an actionable format to empower better business decisions. This IoT platform is a Connecticut-based technology company that develops and delivers IoT technology for the construction industry, including wearable sensors.
Triax Technologies has developed wearable sensors in the form of battery-operated clip-on devices that are being used in ongoing pilot programs with at least 25 large construction firms. These wearable sensors can identify zone-based worker locations and detect free falls. Ultimately, it improves response time by over 90%.
Suggested article for reading: Top 11 Construction Safety Tips for 2023

7. Biometric Wearables
Biometric wearables, essentially wearable sensors, are revolutionizing safety and productivity in the construction industry. These advanced devices are designed to monitor the physiological indicators of workers, providing real-time data about their health and stress levels. Examples of tracked metrics include heart rate, body temperature, and even fatigue levels, which can be measured through subtle variations in movement or responsiveness.
One of the main advantages of wearable sensors in the form of biometric wearables is their ability to improve worker safety. By continuously tracking workers’ vitals, these devices can alert supervisors when stress or fatigue levels become dangerously high. This can help prevent accidents caused by overexertion and ensure that workers get the rest they need.
Additionally, wearable sensors in biometric wearables can play a crucial role in increasing productivity. By monitoring fatigue and stress levels, they can help to optimize work schedules and breaks, ensuring that workers are at their most productive when they’re on the job.
The data collected from these wearable sensors can also provide valuable insights for long-term improvements. Patterns in biometric data can reveal systemic issues that impact worker health and safety, leading to changes that can improve working conditions over time.

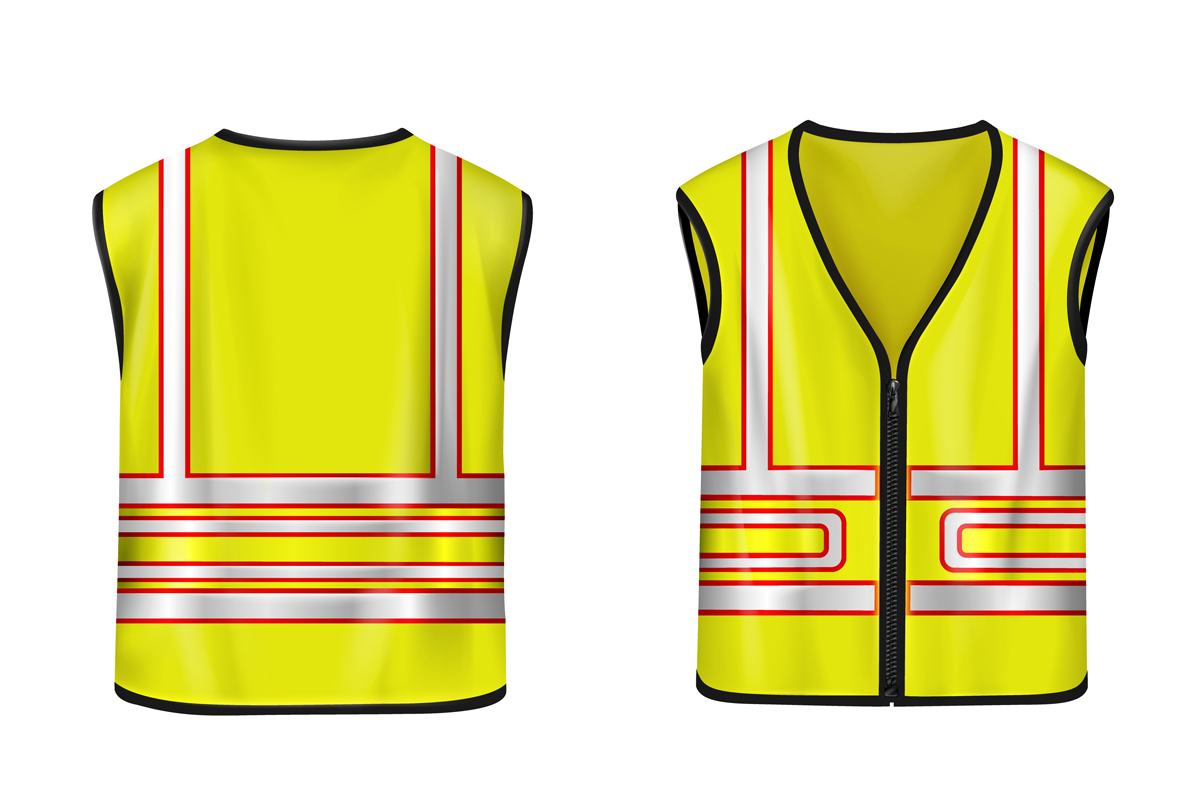
8. Smart vests
Smart vests, a type of wearable sensor technology, represent a significant advancement for the construction industry, blending safety features with health monitoring to ensure optimal worker conditions. These vests come embedded with a variety of sensors that can track location, detect falls, monitor vitals, and more.
The primary purpose of wearable sensors in the form of smart vests is to enhance worker safety. Equipped with GPS tracking, smart vests can precisely locate workers on large construction sites, an essential feature during emergencies. Additionally, fall detection capabilities can trigger immediate alerts, allowing for the swift response to accidents. Some vests are even equipped with automatic inflatable airbags to minimize injury upon detection of a fall.
Beyond safety, wearable sensors in smart vests contribute to the overall health and productivity of workers. Integrated biometric sensors monitor heart rate, body temperature, and other vital signs, providing valuable data about workers’ physical condition throughout the day. High stress or fatigue levels can trigger alerts, allowing management to adjust workloads or schedules to prevent overexertion.
Furthermore, wearable sensors in the form of smart vests can contribute to long-term improvements in work conditions. The continuous collection and analysis of biometric and environmental data can identify patterns related to worker health and safety. These insights can guide changes in operational practices or policies to enhance worker well-being and productivity.

9. Wearable Cameras
Wearable sensors in the form of cameras are becoming increasingly prevalent across various industries, particularly in the realm of construction. These compact, body-worn devices offer the ability to capture first-person perspectives of tasks and events, contributing significantly to safety, productivity, and accountability.
One of the key advantages of wearable sensors such as cameras in construction is their role in enhancing safety. Workers can record their activities, allowing for post-task review and analysis of any safety lapses or near-miss incidents. This footage can be used in training sessions to improve safety practices and reduce future accidents.
Wearable sensors like cameras also boost productivity by allowing for real-time communication and problem-solving. Field workers can stream their point-of-view to supervisors or experts off-site, who can then provide instant feedback or instructions. This reduces downtime and accelerates decision-making.
Additionally, wearable sensors in the form of cameras improve accountability and transparency within construction sites. They can document the construction process, helping to track progress and identify potential issues. In dispute scenarios, video evidence can be pivotal in establishing facts and preventing unnecessary conflicts.
Moreover, these wearable sensors can play a crucial role in knowledge sharing and training. By recording skilled workers performing complex tasks, companies can build a video library for training purposes, thereby preserving and passing on critical skills.

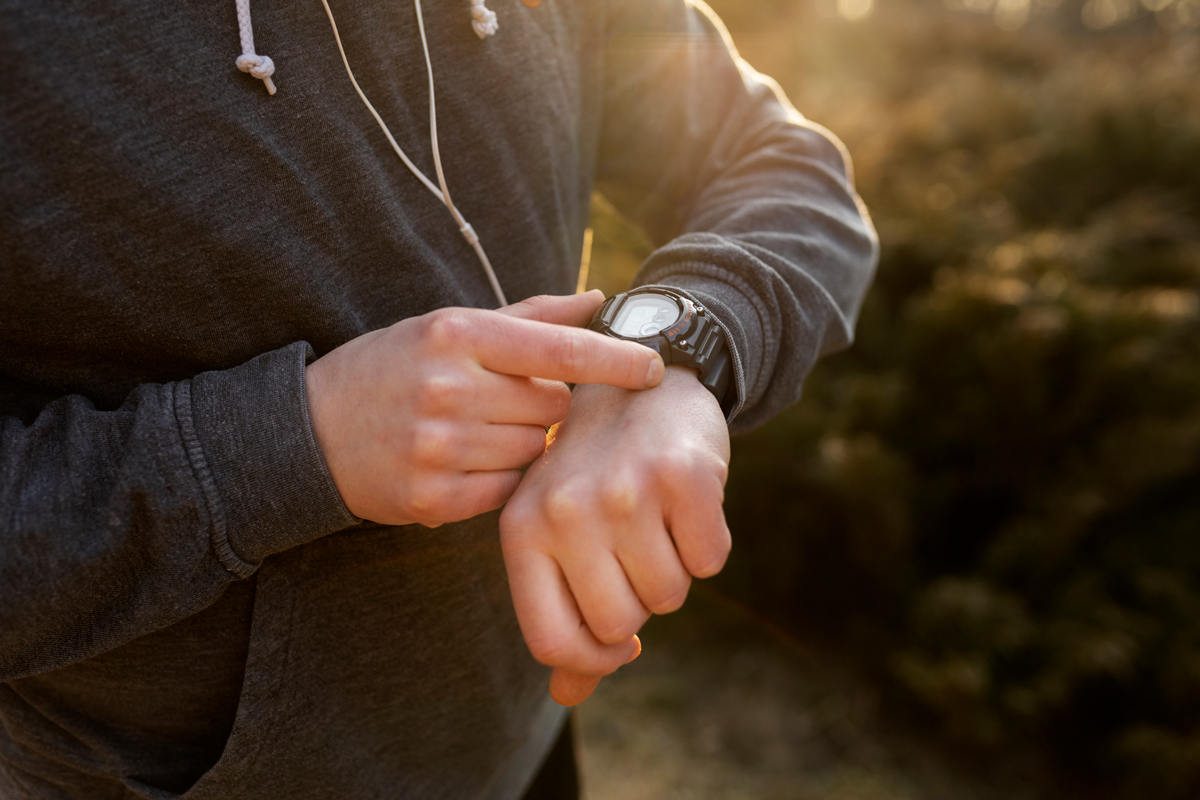
10. Smart Watch
Construction workers often endure tough days at the site. Their job requires substantial physical exertion, including actions like moving, lifting, loading, and building structures. Despite being burdened with these tasks, it’s essential for them to remain focused. However, they also need to stay mindful of time, which can easily be managed by donning a watch!
However, within the tough environment of the construction industry, they need a robust and durable watch, one that can withstand the strain of heavy-duty tasks. Not all watches fit all people; much like there are watches for classy men and casual dudes, there are also sturdy watches designed specifically for the rigors faced by construction workers.
A durable and tough-looking watch isn’t always required to be digital. Some watches maintain a contemporary and stylish appearance, opting for a chain link design instead of a traditional strap. The Citizen Eco-Drive Titanium Perpetual is a prime illustration of such a timepiece.
This exquisite watch not only aids you at the construction site but also enhances your overall appearance with any outfit. The watch features a titanium casing, and for secure attachment, it includes a link bracelet. With its silver hue, the watch adds a significant shine when worn on the wrist.

Future Prospects of Wearable Sensors in Construction
Add a power word to this text: The emerging technology of wearable devices for collecting safety data on construction sites is attracting escalating interest from both researchers and industry professionals. Given the swift progression in wearable device research and their significant potential applications in construction safety, a comprehensive, up-to-date review of research and practical implementations in this area is warranted.
Moving forward, the effectiveness of wearable devices should be enhanced to minimize monitoring discrepancies and to develop affordable systems with commercial advancement potential. Future construction safety might also leverage integrated wearable sensors for multi-parameter monitoring. Indeed, creating an integrated multi-functional wearable system represents another evolving trend. It’s important to acknowledge that certain wearable technologies have been established in other sectors for years but have only recently been applied to construction safety.
Further investigations could explore whether well-developed equipment from other industries can be adapted to suit situations in the realm of construction safety. Discussing its functionality, the watch ensures accurate timekeeping as it syncs across five time zones. It offers water resistance up to 200m, providing strong protection against water pressure.
Suggested article for reading:
Lean Construction Principles and Practical Examples
Top 7 Sustainable Architecture Projects
7 Important Construction Technology 2023
Resources:
For all the pictures: freepik






