The pace of building technologies in construction is advancing, but the industry remains a laggard in digital adoption compared to other traditional physical or infrastructure-intensive industries. Yet with new macroeconomic trends cornering the construction sector, there’s an opportunity for further transformation. The success of ChatGPT and other generative AI tools has also caught the industry’s attention to meet profitability, efficiency and sustainability goals.
The entrance of these cutting-edge building technologies couldn’t come at a better time for construction, which faces a bevy of critical challenges. In the U.S., this includes massive worker shortages amid skyrocketing demand thanks to billions of dollars of government and private investment for new roads, bridges and other critical infrastructure projects.
There is also the ever-changing commercial construction market, which is attempting to reinvent itself in light of post-pandemic social trends, as well as a residential housing market that is sorely in need of new inventory.
Suggested article to read: Smart Building Technology; 2024 Guide
and also: famous architects and their works
Table of Contents
Why is the Traditional Building Industry Evolving?
The factors driving this transition can be pretty fascinating. There are quite a few, but each is significant in its own way, influencing emerging building technologies and their application. The building industry and technology have various complementary aspects, including:
1. Rapidly Changing Client Expectations
Clients are well aware of the continually shifting marketplace. They have higher expectations for more innovatively designed items for their homes, workplaces, commercial structures, and so on. Client demands are rapidly increasing. As a result, you may expect structures to be more flexible, specialized, and energy-efficient, with better security and health characteristics.
2. A Thriving Startup Environment
With new business opportunities created by building technologies, start-ups are increasingly making vital contributions. Oliver Wyman, a global management consultancy, has identified over 1,200 real estate and construction start-ups that have raised more than US$19.4 billion since 2010.
3. Powerful Technological Capabilities
New possibilities have emerged in the construction business. Sensors, as well as the hardware and software that connect to them, are becoming much more affordable, and their rising utilization is improving your operation’s efficiency. With new building technologies in place, construction workers may expect more innovative and valuable transformations, including augmented and virtual reality (AR/VR), drones, robotics, and additive printing.
4. Supportive Legal Frameworks
Digitalization provides a great chance to reduce the environmental impact of construction projects. Given that the construction industry accounts for 38% of worldwide energy-related CO2 emissions, governments around the world are raising CO2 and energy efficiency restrictions for the industry. There will be increased standards for data usage and cybersecurity in construction and infrastructures.
As a construction entrepreneur, you will discover that the coming decade is filled with prospects for innovation, augmentation, and a host of new technical possibilities, all of which will ensure industry success.
5. Emerging Technologists and New-Gen Craftsmen
As construction professionals, you may be aware of the industry’s aversion to change. However, sensibilities are evolving. Modern professionals are more technologically savvy and open to the latest building technologies that the industry offers. With increasing technology-related occupations, the younger generation will have an exciting decade to apply innovation to procedures.
Suggested article to read: What is Building Technology? Type, Example & Everything You Need to Know in 2024
and also read: top construction companies in the philippines
Benefits of Innovative Building Technologies
- Sustainability – Smart buildings are designed to use energy as efficiently as possible under all conditions. Some energy-efficient buildings can create more electricity than they require, saving money and reducing the likelihood of power outages.
- Increased Value – More energy-efficient building technologies help ensure that the building is properly maintained and does not depreciate over time. Furthermore, clever applications can increase the asset’s worth.
- Smart Data – Smart buildings can automatically offer relevant data such as power, heating, ventilation, and air conditioning, water consumption, and more. This data, stored in a centralized data center, can be utilized to recommend corrective actions to reduce wasted energy and assets.
- Eco-friendly – Using smart infrastructure to efficiently use energy does not hurt the environment, and buildings that can create more energy than they consume reduce their footprint even further over time.
- Maximize Work Efficiency – Building technologies can create a healthier, more comfortable, more productive workplace. Advanced lighting and climate controls can greatly improve both lighting and air quality.
- Real-Time Operation – Monitoring and control systems benefit greatly from having access to real-time energy numbers, which allows them to plan and act ahead of time.
- Anticipatory Technology – Building automation, using smart building sensors, may generate alerts if there is a problem with any component of a system. This contributes to predictive facility maintenance, saving time and money.
- Operating Cost Savings – Automatically turning off the lights in a location that is not currently occupied is an example of how automated systems can reduce operating expenses and extend equipment life.
Suggested article to read: Smart Building Solutions in 2024: A Comprehensive Guide

Top Building Technologies for 2025
Here are top 13 building technologies for 2025 you must know about:
1. Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning
Suggested article to read: Artificial Intelligence or AI in Construction Industry; Guide to 2024
Artificial intelligence (AI), like IoT, is a buzzword that has received a lot of attention recently yet is sometimes misinterpreted. AI is the process by which machines or software replicate human behavior and intellect, including the ability to learn and apply knowledge. This enables automation (essentially, decision-making) within the machine or program without requiring human intervention. Machine Learning (ML), which is sometimes used as a synonym for AI, is a technique for implementing AI: it refers to the process by which a machine gains knowledge or skills.
AI has many uses in building technologies, particularly because it is easily coupled with IoT sensors and devices. Such gadgets utilize deep learning to interpret objects and situations hierarchically, making adjustments based on learned user preferences or historical trends.
For example, an AI and IoT-enabled asset management system will detect irregularities in asset operation, such as a leaking refrigerator, based on what it has “learned” about the machine’s energy consumption or output when operating regularly. AI-enabled Service Automation software then forecasts future maintenance and even analyzes and approves work orders with minimal human participation.
2. Building Information Modeling (BIM)
Building Information Modeling (BIM) allows you to record facility information such as blueprints, emergency plans, plumbing, and electrical installations, model them in 3D, and store them digitally for quick access by your employees. Historically, BIM was largely used by AEC (architecture, engineering, and construction) professionals, but it has recently gained popularity in the facilities management setting.
Another extremely useful resource for facility maintenance and ongoing use, BIM functions as a “building handbook” of sorts, providing access to real-time asset profiles as well as improved awareness of asset locations (such as where a specific electrical circuit or piece of machinery is located behind a wall). Aside from geographic information, it offers insights into spatial awareness, light analysis, and the amounts and qualities of building components.
This type of visual and geographical information is extremely useful for facility repairs or renovations. BIM software allows you to “grab” a wall object and move it around to see if it may be placed somewhere else. This technique identifies chances for better space usage and increased building efficiency. Furthermore, BIM enables an infinite number of test scenarios without the need to physically touch the area, resulting in reduced downtime and labor costs.
3. 3D Printing in Construction
3D printing has long been regarded as one of the most significant modern building technologies. However, its future looks even brighter now that the technology has progressed from novelty to emergent industry standard.
With the correct implementation strategy—and some creative thinking—3D printing may help speed up projects, make resources more accessible, and allow you to produce stunning designs.
According to Stephan Mansour, a 3D Printing & Emerging Technology Advisor at MaRiTama Ltd, “Everything can be 3D-printed; it’s just a matter of how far you want to go, how scalable it is, and how much money you’re going to put in.”
In terms of applications, you can utilize 3D printing to make design components such as facades more complicated and detailed. 3D printing can also be used to create construction components such as fixtures and furnishings. This is especially important when dealing with supply shortages or working in faraway locations. Rather than waiting weeks or months for the documents you require, you can have them printed within a few hours or days.
We can expect 3D printing building technologies to mature and grow in the future. As businesses seek to improve quality control, address skilled labor shortages, and experiment with sophisticated ideas, 3D printing will be there to assist them succeed.

4. Internet of Things (IoT)
Smart building technologies use Internet of Things (IoT) systems, which connect various devices via a common Internet Protocol (IP) platform to exchange and analyze information, automatically enhancing each device’s settings. When devices are connected and controlled by sensors, microchips, controllers, and switches, they can begin to communicate and collaborate. This can be used for a variety of purposes, including automatic temperature regulation and emergency system programming.
IoT has gained prominence in “smart home” applications such as self-learning thermostats and smart utility meters. Numerous applications have recently evolved in commercial and industrial contexts to improve internal operations (for example, through IoT-enabled Asset Condition Management) and the occupant experience. Most IoT-enabled devices are controlled and linked over the Internet via a mobile app, making them easy to use. Many executives and facility managers choose to make their buildings more efficient to save money, energy, and downtime. It’s all about people; smart HVAC and lighting will improve the guest and employee experience.
Smart bathrooms are a popular and powerful IoT application in business buildings. Believe it or not, the quality and cleanliness of restrooms (or lack thereof) are the most common complaints from tenants and can easily drive consumers away. IoT sensors tackle problems before they occur: smart soap and paper towel dispensers, for example, digitally inform cleaning personnel when levels are low and can even self-restock as needed. Intelligent occupancy trackers detect when a restroom is full and, via a mobile app, notify guests of the anticipated wait time. On the back end, this type of sensor schedules cleaning teams once a certain amount of people have passed through.
5. Sensor Data
It is critical to keep track of all aspects of your organization, such as people, project sites, and equipment. Proper monitoring facilitates project planning, promotes smoother operations, and ensures that safety and labor regulations are followed.
The good news is that construction sensors and IoT technology make it easier than ever to keep track of your project’s many moving pieces. Various building technologies on the market can help you monitor site conditions, trace supplies through the construction supply chain, increase worker safety, and enable improved facility management.
Sensors are also being used by forward-thinking businesses to foresee and plan for future events. “Using sensor data and Forge as a software foundation, we can predict future product failures,” says Chris Schoneveld, BIM Manager at Alkondor Hengelo.
“So, for a maintenance assignment, we might study a building’s usage curve and protect our products from potential problems. And performing numerous jobs on a single maintenance job reduces our company’s carbon impact by reducing transportation movement.”
6. Artificial Reality (AR)
Augmented reality (AR) is a live, copied view of a real-world environment whose elements are supplemented by computer-generated sensory input. Typically involving a camera and some sort of viewing device – such as a tablet, smartphone, or even eyeglasses – augmented reality superimposes a non-real object onto a view of one’s real, physical surroundings. The maintenance crew we mentioned will not only have the information on-site thanks to BIM, but they will also be able to see it in front of them, using their phone camera.
AR building technologies are particularly effective in facilities management when combined with BIM. Consider putting on a set of AR-enabled glasses (such as the Microsoft HoloLens) while inspecting a plant room full of strange electrical and mechanical equipment. Your glasses, which are programmed with current BIM models, will allow you to see digital representations “hovering” over each piece of equipment, offering identification and more data. This information may include written instructions, warnings, installation dates, and problem-solving building technologies, all of which are extremely important during outages or emergencies.

7. Virtual Reality (VR)
Virtual reality (VR), which was previously regarded to be solely a game technology, is fast expanding into corporate applications. VR extends computer-generated sensor input by shutting off the physical world and transporting the spectator to a realistic, virtual environment, resulting in a fully immersive experience.
VR has already been adopted by the design and construction sectors as a valuable tool during the mockup phase. VR-powered mockups allow a client to experience a proposed building as if they were actually in the space. Before any building begins, the client can walk around, study windows and staircases, and get a sense of the overall experience and flow of the entire project.
Although virtual reality is not yet widely used in the facilities management industry, the technology has gotten increasingly powerful and affordable in recent years. The possible benefits are wide-ranging: VR building technologies enables dynamic quality checks, 3D internal design reviews, and even virtual walkthroughs. VR data can also be incorporated into facilities management software and used for maintenance and operations. Several startups have already begun researching VR in the FM domain. New York-based IrisVR, for example, provides two solutions (desktop software and a mobile app) that integrate 3D BIM models into VR to enable 1:1 collaboration and design review.
8. Prefabrication, Modularization, and Sustainability
There will be a growing tendency toward multi-trade prefabrication building technologies. For example, in Dubai, construction professionals printed a 3D office structure in about 17 days before constructing it on-site for two days. Prefabrication can help you save money. Construction experts can take advantage of bulk material reductions. Saving time is an additional benefit. With its benefits, professionals have used prefabrication on some of the UAE’s most outstanding projects, including the Dubai Mall and the Dubai Opera.
Another intriguing trend is off-site construction, often known as modularization, which is quite similar to prefabrication. With the promise of uniform quality and speedier construction timelines, the technology can generate structures that are comparable to their traditionally built equivalents. Another outstanding example is a two-day precast house, which reflects the Saudi government’s goals of accelerating innovation and encouraging homeownership in the kingdom. The one-story property in Riyadh was built with modular concrete by a local company.
As a result, forward-thinking construction firms have already begun implementing these tactics in their operations. Standardization of new building technologies reduce costs and lead times. The approaches also have the advantage of being environmentally benign, as any leftover construction materials can be easily recycled.
Suggested article to read: Sustainable Construction Technology; Ultimate Guide in 2024
also read: Mega Projects: Top 17 Largest Construction Projects Reviewed

9. Sustainable Building Materials
As the construction sector seeks to cut carbon emissions, it is shifting toward more sustainable building technologies. This involves the use of sustainable building materials such as cross-laminated timber, reclaimed wood, bamboo, recycled rubber, and a variety of other novel materials. Consider a structure composed of straw bales, rammed earth, hempcrete (a concrete-like material manufactured from hemp plants), or ferrock (a concrete-like material made from steel particles). Some of these materials can absorb and trap carbon dioxide, making them carbon-neutral.
Using sustainable building materials is not only beneficial for the environment; it may also lower construction costs, enhance structural energy efficiency, and boost property value. Operational costs are decreased by 5 to 15%, depending on the green material used. There are also regulatory incentives in some locations that make sustainable construction more appealing.
Buildings created from sustainable materials are in high demand. They frequently have higher occupancy and rental rates than traditional-built structures. Green building materials may also help to improve occupant health. When it comes to green construction, everyone benefits: the industry, the tenants, and the environment.
10. Digital Twins & Digital As-Builts
Though the word was coined in 2002, the idea of digital twins and digital as-builts has been around for decades. NASA was among the first to employ a version of the technology in the 1960s. Most importantly, engineers tried solutions on a digital simulation of Apollo 13 to prevent another disaster.
The use of digital twins in the construction sector is increasing as project teams transition away from manual, time-consuming documentation. A digital twin, also known as a digital as-built, is a virtual counterpart of a physical object that provides real-time data during the whole construction and maintenance process. These digital representations can be used to calculate carbon footprints, simulate situations, and collect real-time data from installed sensors.
Owners employ digital twins and as-builts to acquire design and construction information, allowing them to make more timely decisions about operating and maintenance expenses. On-site digital twins and as-builts provide material and labor forecasting.
In the future, digital twins and as-builts may become autonomous, learning and acting on behalf of their users. Today, thanks to Building Information Modeling (BIM), they are proving to be an important element of the construction industry’s digital transition.
11. Building Automation
Building Automation is a comprehensive infrastructure that enables centralized control of a building’s HVAC, lighting, security, and other systems. A central digital or mobile hub, known as a Building Management System (BMS) or Building Automation System (BAS), controls building automation. These systems are also compatible with IoT solutions and can monitor and control critical parameters such as temperature, humidity, energy, and water pressure.
Building Automation has several advantages, including increased energy efficiency, lower operating costs, and improved occupant comfort. Smart building technologies produce a better, more pleasant work environment, which swiftly leads to increased productivity. A Building Automation System, for example, could be set to turn up the air conditioning and ventilation in a specific conference room when it detects that someone has turned on the lights. It even integrates AI and IoT technology, “learning,” for example, that this conference room is utilized from 10:00 -11:00 a.m. every Tuesday and then altering its climate settings few minutes in advance.
Building automation also ensures that your facilities meet all industry standards. With smart sensors, you’ll always know what’s going on around your premises. You will be able to make timely improvements and changes to ensure that your facilities consistently satisfy the highest compliance standards.
12. Robotic Total Station (RTS)
The typical method of laying out building technologies on a site entails a team using architectural drawings, a tape measure, a spirit level, and a theodolite (a precision tool for measuring angles) to determine attachment sites for cable trays and pipework.
This approach, however, does not perform well for increasingly complex structures. It is time-consuming and laborious, with a large margin for error, which can have major repercussions, such as collisions with other building technologies and prefabricated systems that do not fit, resulting in time, money, and material waste.
Robotic Total Stations (RTS) are electronic theodolites with electronic distance measurement capabilities that may be controlled remotely. The layout can be accomplished by a single person using a tablet and the appropriate software, with RTS providing higher efficiency, improved accuracy, less mistakes, and less paperwork, as well as lower labor costs.
13. Cloud and Mobile Technology
Cloud operating systems are already employed in a variety of businesses. Today, with mobile devices that leverage cloud building technologies (anywhere, anytime), you may store and exchange large volumes of data quickly. To stay competitive, you may need to use a cloud-based enterprise phone system that is easily accessible.
Cloud solutions can not only help to store vast volumes of data but also make it accessible to project managers while keeping it secure in a remote location. Later, this data can be retrieved by connected devices or data analysis systems. So, powerful data processing and storage are just two of the advantages of cloud computing building technologies, but the latter might be important for businesses to meet contractual responsibilities.
Suggested article to read: 11 Types of Important Construction Technology in 2024
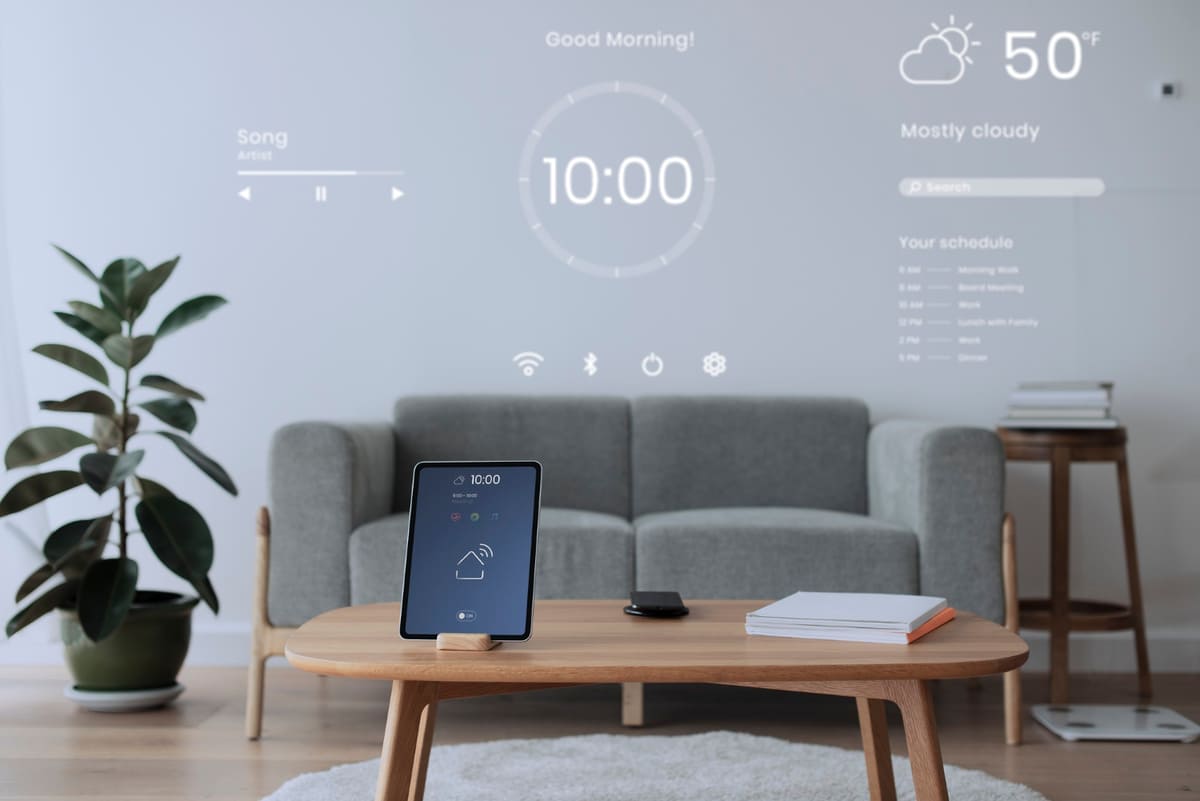
Common Smart Building Technologies and Products
There are numerous smart building technologies accessible to businesses today, but not all of them are required, depending on the aims of your building and organization. IoT smart building designs for commercial properties should include goods that have the greatest influence on enhancing efficiency, fostering collaboration, and providing a safe, secure environment. The most prevalent smart building technology that can assist managers with this include:
1. Smart Lighting Building Technologies
Smart lighting solutions use sensors to turn lights on and off based on occupancy. Lighting controls can be combined with automated blinds or daylight sensors to optimize natural light while lowering lighting expenses. In commercial smart building technologies, the intelligent lighting solution would be designed to reduce non-safety lighting after business hours. In a multi-unit residential smart building, lighting would be regulated exclusively in public or shared areas based on ambient light conditions or safety and security requirements. Some multi-unit complexes may also offer smart building IoT solutions for individual apartments.
2. Smart HVAC Systems
Smart HVAC building technologies automate the regulation of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems, altering temperatures based on occupancy, current temperatures, and weather forecasts to save energy usage and maintain a comfortable environment.
3. Smart Windows
Smart Windows that lighten or darken in response to sunlight intensity can minimize the demand on lighting and HVAC systems while also reducing glare.
4. Sensors
Smart sensors monitor the surroundings for irregularities that require the attention of security professionals. Building technologies devices may monitor air quality, temperature, humidity, and occupancy levels while also detecting vapes, smoke, loud noises, and movements, alerting operators to potential safety and security issues. These smart building technologies improve situational awareness, including in privacy-sensitive areas, increase safety, and provide information that can assist building managers in creating a healthier environment for inhabitants.
5. Preventative Maintenance Systems
Preventative Maintenance Systems utilize strong analytics and artificial intelligence on system data to spot abnormal patterns in performance and send out maintenance notifications. Facility management staff can resolve issues before they cause outages or downtime, thanks to smart building software and apps that can provide additional information on system performance.
6. Meeting Room Booking Systems
Meeting room booking systems integrate room management systems with employee calendars, meeting schedules, and planned customer visits, providing facility managers with complete visibility into space availability. Integrating booking systems with smart environmental controls and access control ensures that light, air conditioning, and heating systems are only activated when a room is filled and that only people who have reserved a space have access to the facility.
7. Desk Management Software
Desk management software is vital for hybrid offices, as workspace need vary on a daily basis. Employees can reserve workstations in advance for planned visits or look for available desks if they need to make an unplanned visit. This IoT building automation is integrated with intelligent access control and only permits admission on the days and times specified in the reservation.
Suggested article to read: Exploring 7 Construction Innovation Ideas of 2024

Creating Smart Building Technologies Solution Plan
Smart building technologies can be included into new construction, or a smart infrastructure can be retrofitted into existing homes. Use this guide to help you create a comprehensive smart building plan for your facility.
1. Planning and Budgeting
During the planning stage, proposals should be shared with all stakeholders, including owners, property and building managers, and tenants, to determine needs and priorities. While there are numerous smart building technologies that can improve energy efficiency and the building environment, it is critical to select and prioritize the smart building IoT solutions that will provide the most value.
It is also beneficial to engage technology and security professionals with experience in intelligent building design, since this can help to avoid costly mistakes.
Your basic smart building technologies plan should include:
- The number and location of sensors and IoT devices
- Networking and power supply infrastructure
- Management and control software
- The quantity and location of access control components and security cameras
Budgets for smart building IoT solutions should include the expenses of installation, integration, long-term maintenance, and upgrade fees as a basis for estimating through-life costs. Setting measurements for the intended installation is critical to assessing the solution’s benefits and calculating return on investment.
2. Selecting Smart Building Technology Products
The smart building technologies components must be interoperable and easy to integrate so that they can function as a single system. As a result, it is critical to choose goods and systems that are designed and constructed to meet open standards. The smart building components must also be dependable so that they cause minimal disturbance to normal operations.
When deciding which smart building technologies to invest in, look for solutions that provide long-term flexibility, including the ability to scale up or down. Based on the data provided by your smart building technologies, you can quickly change your plans in the future. Intelligent building technology is constantly evolving, so incorporating flexibility into your plans from the start can help future-proof your investment.
3. Software Selection
Smart building software for managing and operating the system can be installed on-site or hosted in the cloud. Cloud-based software allows for better flexibility, scalability, and remote management via Internet-connected mobile devices. Cloud hosting also includes automatic software updates and maintenance, allowing the facility management team to focus on system operations while reducing downtime for in-person maintenance.
4. Installation and Integration
New and existing system components, such as lighting, HVAC, access control, and security products, should be installed and linked to the appropriate sensors. Wherever practical, complimentary smart building technologies, such as security cameras and motion sensors, should be included to optimize overall system performance.
5. Connectivity and Power
System components can be connected to smart building management systems and powered via dedicated cabling, data networks, or wireless networks. Direct cabling is the most expensive option, lacks the flexibility of network connections, but is typically the most reliable.
Data networks enable excellent two-way communication between components and controllers and can provide power using Power over Ethernet (PoE) technology. Wireless networks enable connectivity, but the network must have adequate signal strength across the facility to provide consistent, dependable operation.
6. Analytics and AI
Analytics software should be connected with smart building control systems so that sensor data may be automatically interpreted and relevant responses initiated. Administrators should establish rules that govern response, for as setting time of day guidelines for lighting or HVAC controls in a commercial facility. Incorporating artificial intelligence into individual components or the central management system can increase accuracy and reaction by detecting unexpected patterns or events that demand investigation or action.
7. Integrated System Security
Smart infrastructures rely on secure data flow to efficiently control and operate building technologies. This makes it critical to safeguard the infrastructure and data against physical or cyber threats that could undermine the system. An integrated security plan guarantees that both physical and cyber security teams are aware of potential threats by sharing security data and coordinating coverage to prevent security gaps.
10 Best Construction Companies in the World Using Tuilding Technologies
Suggested article to read: Top 13 Smart Building Companies in the World; 2024 Review
1. China State Construction Engineering Corporation (CSCEC)
- Location: Beijing, China
- Employees: 335,000
- Revenue: ¥203 billion
- Founded: 1957
- Notable Projects: Shanghai World Financial Center
CSCEC has its headquarters in Beijing and is a Fortune Global 500 corporation. CSCEC is well-known for its work on large-scale infrastructure projects, including highways, bridges, power plants, and airports by using cutting-edge building technologies. It also offers engineering services for buildings and industrial facilities. CSCEC is the world’s largest construction company by revenue and the eighth largest general contractor in terms of international sales.
2 – Samsung C&T Corporation
- Location: Seoul, South Korea (Global presence, including France)
- Employees: ~17,000
- Revenue: Not explicitly stated (Refer to financial reports)
- Founded: 1938 (as Samsung Sanghoe), reorganized in 1951
- Notable Projects: Burj Khalifa, Merdeka 118, Riyadh Metro, Fujairah F3 Power Plant, Qatar Desalination & Power Plant
Samsung C&T Corporation was formed in 1938 and is headquartered in Seoul. As one of Asia’s major construction enterprises, it specializes in civil engineering projects like roads, bridges, dams, and hydropower plants making use of building technologies. In addition to large-scale civil works projects, Samsung C&T also provides property development and engineering services for buildings and factories.
3 – Vinci SA
- Location: Rueil Malmaison, France
- Employees: 222,000
- Revenue: €48.05 billion
- Founded: 1899
- Notable Project: Louvre Entrance
Alexandre Giros and Louis Loucheur formed Vinci SA, a French corporation situated in Rueil Malmaison outside Paris, in 1899. Vinci SA is one of the world’s largest construction corporations, with global operations and annual revenues of more than $53 billion USD. Its primary focus areas are transportation infrastructure (roads, trains, and airports) and energy production (nuclear power plants and renewable energy sources). Vinci SA also provides services for property development and management, as well as waste management solutions.
4 – China Railway Construction Corporation Limited (CRCC)
- Location: Beijing, China
- Employees: ~267,587 (as of 2023)
- Revenue: ¥1.25 trillion (~$152 billion USD, 2023)
- Founded: 1948
- Notable Projects: High-Speed Railway in Southeast Asia, Metro Construction in South America
CRCC has its headquarters in Beijing and is one of China’s oldest state-owned corporations, founded in 1907 by Sun Yat-sen for railway building across China’s regions during his presidency from 1912 to 1925. Since then, CRCC has expanded into overseas markets, providing services related to railway engineering design and construction, as well as bridge building and urban rail transit systems throughout many countries, including Russia and South Africa, among others; however, its main focus remains within China’s borders, where it has completed many major railway projects connecting cities across all provinces since the 1990s until today, making it one of the top four largest contractors.

5 – Bechtel Group Incorporated
- Location: Reston, Virginia, USA’
- Employees: Approximately 55,000
datanyze.com - Revenue: $16.8 billion (2022)
- Founded: 1898
- Notable Projects: Hoover Dam, Channel Tunnel, Boston Central Artery/Tunnel Project (“Big Dig”)
Established in 1898 by Warren A Bechtel, this American multinational engineering firm headquartered in San Francisco, California, specializes in oil and gas pipelines as well as other complex civil works such as tunnels, dams, airports, and so on; its client base ranges from governments to private corporations, having completed various major public works in the United States, Iraq, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, India, and the United Kingdom, among others, earning huge revenues of up to $17.6 billion per year.
6 – Skanska AB
- Location: Stockholm, Sweden
- Employees: 31,000
- Revenue: KR160.3 billion
- Founded: 1887
- Notable Project: MetLife Stadium
Skanska AB is a Swedish multinational construction and development corporation. Skanska is the world’s fifth-largest construction corporation, offering both commercial and residential real estate development services, as well as engineering contracting activities in areas such as transportation, infrastructure, healthcare facilities, and educational structures using smart building technologies. Its portfolio also includes a number of important bridges, roads, tunnels, power plants, and wastewater treatment facilities.
7 – Bouygues S A
- Location: Paris, France
- Employees: 130,500
- Revenue: €35.55 billion
- Founded: 1952
- Notable Project: Musée d’Orsay
Set up 1952. Bouygues S A is a French manufacturing group with its headquarters in Paris’ 8th arrondissement. Bouygues trades on the Euronext Paris platform and is a blue chip in the CAC 40 stock market index. The group focuses on construction (Colas Group and Bouygues Construction), real estate development (Bouygues Immobilier), media (TF1 Group), and telecoms (Bouygues Telecom).Over the last few years, the firm has focused mostly on government military defense initiatives.
8 – ACS Actividades de Construcción y Servicios SA
- Location: Madrid, Spain
- Employees: 190,500
- Revenue: €39 billion
- Founded: 1997
- Notable Project: Torre Glòries
This Spanish international group was founded in 1997 and focuses on four business divisions: civil infrastructures, energy, the environment, and telecommunications, which provide services primarily related to tunneling, mining, concrete prefabricated structures, and public housing complexes, among others. Currently, its annual revenues are around 27.8 billion Euros.
9 – Kiewit Corporation
- Location: Omaha, Nebraska, USA
- Employees: Approximately 31,100 (2023)
- Revenue: $17.1 billion (2023)
- Founded: 1884
- Notable Projects:
-
- Hoover Dam Bypass Bridge
- Alaskan Way Viaduct Replacement Tunnel in Seattle
- TD Ameritrade Park
- NCAA’s College World Series facilities
Kiewit Corporation is an American construction business formed in 1884 and headquartered in Omaha, Nebraska. In 2021, it was placed 243rd in the Fortune 500. It is a privately held company and one of North America’s largest construction and engineering firms getting use of building technologies. It is an employee-owned business. Kiewit specializes in mine management, production, infrastructure building, maintenance, and contract mining projects. It has an annual revenue of approximately 10.3 billion US dollars.
10 – Hochtief AG
- Location: Essen, Germany
- Employees: 47,000
- Revenue: €21.1 billion
- Founded: 1874
- Notable Project: Bosphorus Bridge
Hochtief AG is a German construction firm integrating building technologies, headquartered in Essen, North Rhine-Westphalia. Hochtief is Germany’s largest construction firm that works abroad. It is one of the top general construction companies in the United States through its Turner subsidiary and in Australia through a 90% stake in the CIMIC Group. In 2010, it employed over 70,000 people across five company divisions. Hochtief Concessions is a significant airport operator. The others are responsible for construction project planning, finance, construction, and operations.
Looking to the Future
New building technologies appears to be the stuff of Star Trek fiction. Many advancements are at least 30 years in the making. Document management and design collaboration are not new. What is new is the rate of change and the increasing demand for efficiency.
All engineers and construction professionals are concerned with time and cost savings. Tools that leverage data from previous and present projects can assist reduce project risk. Keeping track of and restricting modifications during construction is difficult. Real-time mobile apps reduce the pressure of frequent change.
Camera technology offers new ways to monitor and improve safety. Advanced camera deployment functions as eyes and ears. This is especially true in tough, inaccessible, or dangerous regions. Cameras and other monitoring systems ensure that job site losses are kept to a minimum.
Even more futuristic building technologies show promise in building. Ideas derived from entertainment, medicine, and other fields are used. Artificial intelligence, virtual and augmented reality for construction are all extremely near together. These additions are achievable because to modern wearable technology and 3D printing.
FAQs
Why is the traditional building industry evolving?
- Answer: The variables influencing this transformation can be rather fascinating. There are quite a few, but each is significant in its own way, influencing emerging building technologies and their application. The building industry and technology are compatible in several ways, including quickly changing client expectations, a strong startup ecosystem, tremendous technological capabilities, supportive legislative frameworks, and budding technologists and new-generation craftsmen.
What are the benefits of innovative building technologies?
- Answer: Sustainability – Smart buildings are intended to use energy as efficiently as possible in all conditions. Some energy-efficient buildings can generate more electricity than they use, saving money and lowering the risk of power outages. Increased Value – More energy-efficient building technologies assist ensure that the structure is well-maintained and does not depreciate over time. Furthermore, smart uses can raise the asset’s value.
What are the top building technologies for 2025?
- Answer: Some of the most impactful ones include Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning, Building Information Modeling (BIM), 3D printing in construction, Sensor Data, Artificial Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), Prefabrication, Modularization, Sustainable Building Materials, Digital Twins & Digital As-Builts, Building Automation, Robotic Total Station (RTS), Cloud and Mobile Technology and the Internet of Things (IoT). These technologies are transforming the industry by improving efficiency, sustainability, and automation in construction and facility management.
What are some examples of building technologies used by top construction companies?
- Answer: Top construction businesses are embracing a variety of building technologies to improve their operations. For example, China State Construction Engineering Corporation (CSCEC) uses cutting-edge building technologies for large-scale infrastructure projects like highways, bridges, power plants, and airports. Samsung C&T Corporation employs building technology for civil engineering projects such as highways, bridges, dams, and hydropower plants. Vinci SA also focuses on transportation infrastructure and energy generation projects that utilize cutting-edge building technology.
How are AI and virtual reality shaping the future of construction using building technologies?
- Answer: Artificial intelligence, virtual reality, and augmented reality are revolutionizing construction through the employment of modern building technologies. Modern wearable technology and 3D printing have brought these building technologies very close to being deployed. AI is improving project efficiency and safety, while virtual and augmented reality are being used for project planning and monitoring, providing new ways to visualize and optimize construction processes.
How are construction companies using smart building technologies to promote sustainability?
- Answer: Smart building technologies are at the heart of the construction sustainability movement. These building technologies make use of IoT (Internet of Things) devices to improve energy efficiency, minimize waste, and cut carbon footprints. As cities grow, these environmentally friendly technologies will become increasingly vital in creating more sustainable and energy-efficient buildings.
Conclusion
It’s a fascinating moment to work with building technologies. It is critical that we all work together to develop clear strategies based on the pain points and issues that members of our sector confront. Just because we have the potential to disrupt the industry does not imply we should. We can easily add building technologies such as AI into our existing solutions to increase their efficiency and usefulness. The industry has tremendous potential for growth, and I am thrilled to be at the forefront of it with our industry partners and customers.
The Role of Data Analytics in Construction Management 2025
What is ConTech (Construction Technology)? 2025 Review + Examples
Top 8 Green Buildings in the Philippines Leading the Sustainability Movement
13 Best UK Architecture Firms You Should Know About in 2025
Sustainable Construction Firms in the USA: Which are the Top 7?
Top 12 Boutique Architecture Firms: Small Studios Making a Big Impact
Resources:
buildingradar | autodesk | constructible.trimble | mobilevideoguard | bechtel | skanska | virtusa | avigilon | letsbuild | planradar | indeed | imaginovation | forbes | servicechannel
For all the pictures: Freepik



